read 07
Introducing CSS
- What CSS does
CSS allows you to create rules that specify how the content of an element should appear. For example, you can specify that the background of the page is cream, all paragraphs should appear in gray using the Arial typeface, or that all level one headings should be in a blue, italic, Times typeface
X Rules, properties, and values
Example Styles
- Boxes: Width and height Borders (color, width, and style) Background color and images Position in the browser window.
- Text:Typeface Size,Color ,Italics, bold, uppercase, lowercase, small-caps
- Specific:There are also specific ways in which you can style certain elements such as lists, tables, and forms.
- X How CSS works CSS works by associating rules with HTML elements. These rules govern how the content of specified elements should be displayed. A CSS rule contains two parts: a selector and a declaration. CSS Associates Style rules with HTML elements,Selector ==>p { font-family: Arial;}<==Declaration

CSS declarations sit inside curly brackets and each is made up of two parts: a property and a value, separated by a colon. You can specify several properties in onedeclaration, each separated by a semi-colon.
element to indicate where the CSS file is located
- <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head>
</head>
From Garden to Plate
A potager is a French term for an ornamental vegetable or kitchen garden ...
What to Plant
Plants are chosen as much for their functionality as for their color and form ...
</html> body { font-family: Arial, Verdana, sans-serif;} h1, h2 { color: #ee3e80;} p { color: #665544;}
Using External CSS
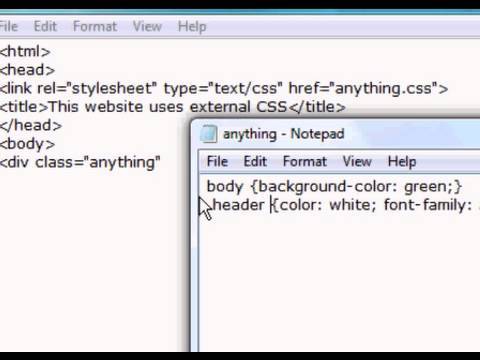
Using Internal CSS

Different versions of CSS & Browser Quirks CSS1 was released in 1996 and CSS2 followed two years later. Work on CSS3 has been ongoing but the major browsers have already started to implement it.
- CSS treats each HTML element as if it appears inside its own box and uses rules to indicate how that element should look.
- X Rules are made up of selectors (that specify the elements the rule applies to) and declarations (that indicate what these elements should look like).
- X Different types of selectors allow you to target your rules at different elements.
- X Declarations are made up of two parts: the properties of the element that you want to change, and the values of those properties. For example, the font-family property sets the choice of font, and the value arial specifies Arial as the preferred typeface.
- X CSS rules usually appear in a separate document, although they may appear within an HTML page.
The color property allows you to specify the color of text inside an element. You can specify any color in CSS in one of three ways:
- rgb values These express colors in terms of how much red, green and blue are used to make it up. For example: rgb(100,100,90)
- hex codes These are six-digit codes that represent the amount of red, green and blue in a color, preceded by a pound or hash # sign. For example: #ee3e80 color
- names There are 147 predefined color names that are recognized by browsers. For example: DarkCyan
Every color on a computer screen is created by mixing amounts of red, green, and blue. To find the color you want you can use a color picker.
CSS3: HSL Colors
CSS3 introduces an entirely new and intuitive way to specify colors using hue, saturation, and lightness values.
- hue Hue is the colloquial idea of color. In HSL colors, hue is often represented as a color circle where the angle represents the color, although it may also be shown as a slider with values from 0 to 360.
- saturation Saturation is the amount of gray in a color. Saturation is represented as a percentage. 100% is full saturation and 0% is a shade of gray.
-
lightness Lightness is the amount of white (lightness) or black (darkness) in a color. Lightness is represented as a percentage. 0% lightness is black, 100% lightness is white, and 50% lightness is normal. Lightness is sometimes referred to as luminosity
- It is important to ensure that there is enough contrast between any text and the background color (otherwise people will not be able to read your content).
- X CSS3 has introduced an extra value for RGB colors to indicate opacity. It is known as RGBA.
- X CSS3 also allows you to specify colors as HSL values, with an optional opacity value. It is known as HSLA.