class07
Domain Modeling
Domain modeling is the process of creating a conceptual model in code for a specific problem. A model describes the various entities, their attributes and behaviors, as well as the constraints that govern the problem domain. An entity that stores data in properties and encapsulates behaviors in methods is commonly referred to as an object-oriented model.
A domain model that’s articulated well can verify and validate the understanding of a specific problem among various stakeholders. As a communication tool, it defines a vocabulary that can be used within and between both technical and business teams.
- Define a constructor and initialize properties To define the same properties between many objects, you’ll want to use a constructor function.
Generate random numbers
To model the random nature of user behavior, you’ll need the help of a random number generator. Fortunately, the JavaScript standard library includes a Math.random() function for just this sort of occasion.
Domain modeling is the process of creating a conceptual model for a specific problem. And a domain model that’s articulated well can verify and validate your understanding of that problem. Some tips to follow when building your own domain models.
- When modeling a single entity that’ll have many instances, build self-contained objects with the same attributes and behaviors.
- Model its attributes with a constructor function that defines and initializes properties.
- Model its behaviors with small methods that focus on doing one job well.
- Create instances using the new keyword followed by a call to a constructor function.
- Store the newly created object in a variable so you can access its properties and methods from outside.
- Use the this variable within methods so you can access the object’s properties and methods from inside.
Tables
What’s a Table? A table represents information in a grid format. Examples of tables include financial reports, TV schedules, and sports results
The table element is used to create a table.The contents of the table are written out row by row.
the tr You indicate the start of each row using the opening tr tag. (The tr stands for table row.) It is followed by one or more the td elements (one for each cell in that row). At the end of the row you use a closing tr tag thetd tag Each cell of a table is represented using a td element. (The td stands for table data.) At the end of each cell you use a closing td tag
Table Headings
The th element is used just like the td element but its purpose is to represent the heading for either a column or a row. (The th stands for table heading.) Even if a cell has no content, you should still use a td or th element to represent the presence of an empty cell otherwise the table will not render correctly. (The first cell in the first row of this example shows an empty cell.)
Spanning ColumnS and Rows:
You can make cells of a table span more than one row or column using the rowspan and colspan attributes.
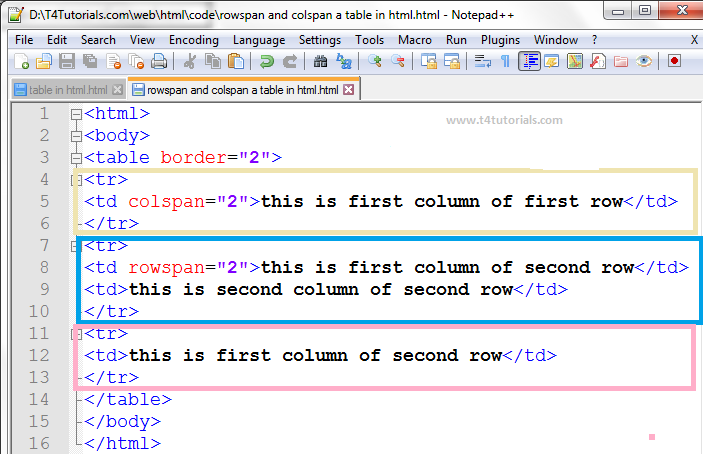

For long tables you can split the table into a thead, tbody, and tfoot


- CREATING OBJECTS USING CONSTRUCTOR SYNTAX

ADDING AND REMOVING PROPERTIES
Once you have created an object (using literal or constructor notation), you can add new properties to it. You do this using the dot notation
CREATE THE OBJECT, THEN ADD PROPERTIES & METHODS
The object is created on the first line of the code sample. The properties and methods are then added to it afterwards. Once you have created an object, the syntax for adding or removing any properties and methods from that object is the same.
LITERAL NOTATION
OBJECT CONSTRUCTOR NOTATION
THIS (IT IS A KEYWORD) The keyword this is commonly used inside functions and objects. Where the function is declared alters what this means. It always refers to one object, usually the object in which the function operates.
STORING DATA
In JavaScript, data is represented using name/value pairs. To organize your data, you can use an array or object to group a set of related values. In arrays and objects the name is also known as a key.
ARRAYS ARE OBJECTS
Arrays are actually a special type of object. They hold a related set of key/value pairs , but the key for each value is its index number

THREE GROUPS OF BULT-IN OBJECTS
THE BROWSER OBJECT MODEL: THE WINDOW OBJECT The window object represents the current browser window or tab. It is the topmost object in the Browser Object Model, and it contains other objects that tell you about the browser.
THE DOCUMENT OBJECT MODEL:
THE DOCUMENT OBJECT The topmost object in the Document Object Model (or DOM) is the document object. It represents the web page loaded into the current browser window or tab.
GLOBAL OBJECTS:
STRING O BJECT Whenever you have a value that is a string, you can use the properties and methods of the String object on that value. This example stores the phrase “Home sweet home “ in a variable.
DATA TYPES REVISITED
In JavaScript there are six data types: Five of them are described as simple (or primitive) data types. The sixth is the object (and is referred to as a complex data type).
SIMPLE OR PRIMITIVE DATA TYPES JavaScript has five simple (or primitive) data types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
- Undefined (a variable that has been declared, but no value has been assigned to it yet)
- Null (a variable with no value - it may have had one at some point, but no longer has a value)
- 0bject Under the hood, arrays and functions are considered types of objects.
FUNCTIONS ARE OBJECTS Technically, functions are also objects. But they have an additional feature: they are callable, which means you can tell the interpreter when you want to execute the statements that it contains.
GLOBAL OBJECTS: NUMBER OBJECT
Whenever you have a value that is a number, you can use the methods and properties of the Number object on it.
WORKING WITH DECIMAL NUMBERS
As with the String object the properties and methods of the Number object can be used with with any value that is a number.
GLOBAL OBJECTS: MATH OBJECT
The Math object has properties and methods for mathematical constants and functions.
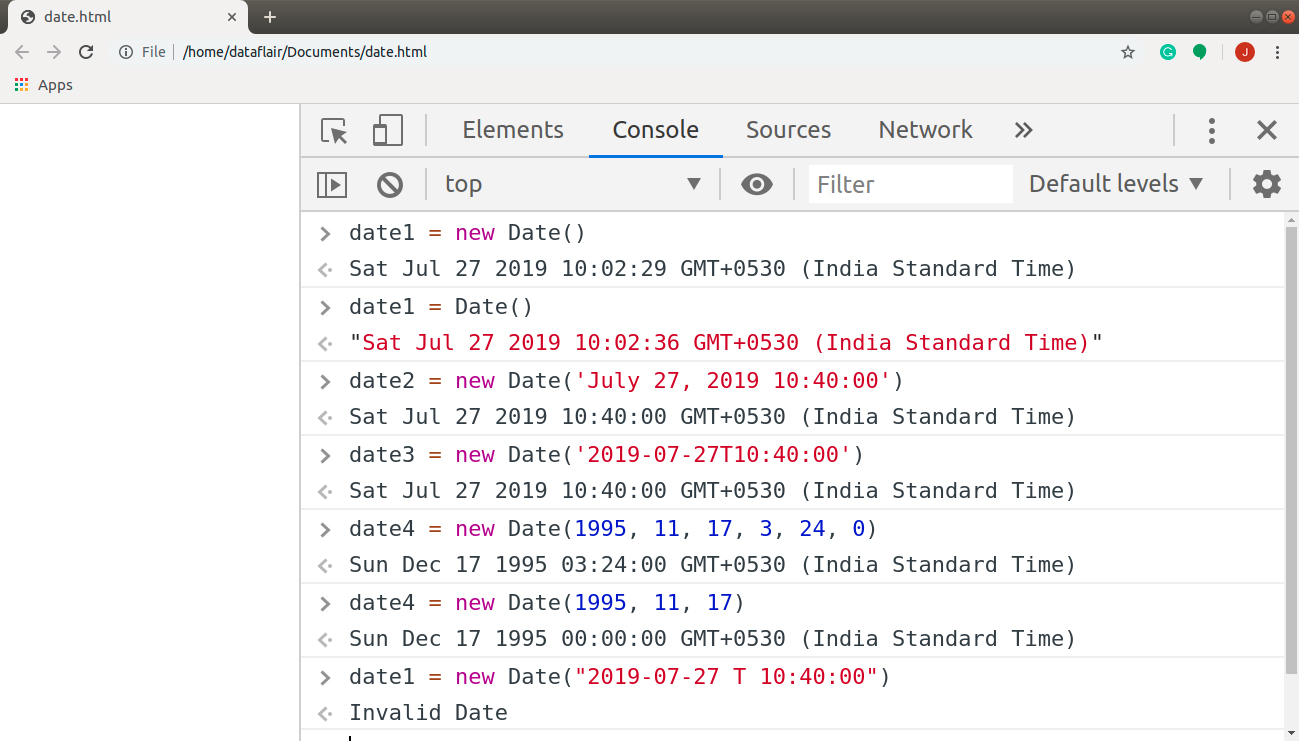
GLOBAL OBJECTS: DATE OBJECT
(AND TIME) Once you have created a Date object, the following let you set and retrieve the time and date.
An object is a series of variables and functions that represent something from the world around you. Arrays and objects can be used to create complex data sets (and both can contain the other).