class-03
Lists
There are three types of HTML lists:
- The ordered list is created with the ol element.
- li Each item in the list is placed between an opening li tag and a closing li tag. (The listands for list item.)
- Unordered Lists :The unordered list is created with the ul element.
- li Each item in the list is placed between an opening li tag and a closing li tag. (The listands for list item.)

- Definition Lists:The definition list is created with the dl element and usually consists of a series of terms and their definitions.
- Inside the dl element you will usually see pairs of dt and dd elements. dt This is used to contain the term being defined (the definition term) dd This is used to contain the definition.
- Nested Lists:You can put a second list inside an li element to create a sublist or nested list
Box Dimensions
width, height By default a box is sized just big enough to hold its contents. To set your own dimensions for a box you can use the height and width properties. The most popular ways to specify the size of a box are to use pixels, percentages, or ems. Traditionally, pixels have been the most popular method because they allow designers to accurately control their size
- Limiting Width
min-width, max-width Some page designs expand and shrink to fit the size of the user’s screen. In such designs, the min-width property specifies the smallest size a box can be displayed at when the browser window is narrow, and the max-width property indicates the maximum width a box can stretch to when the browser window is wide
- Limiting Height
min-height, max-height
-
Overflowing Content: overflow The overflow property tells the browser what to do if the content contained within a box is larger than the box itself. It can have one of two values: hidden This property simply hides any extra content that does not fit in the box. scroll This property adds a scrollbar to the box so that users can scroll to see the missing content.
- Border, Margin & Padding Every box has three available properties that can be adjusted to control its appearance: Border Every box has a border (even if it is not visible or is specified to be 0 pixels wide). The border separates the edge of one box from another. 2 Margin Margins sit outside the edge of the border. You can set the width of a margin to create a gap between the borders of two adjacent boxes. 3 Padding Padding is the space between the border of a box and any content contained within it. Adding padding can increase e the readability of its contents
White space & Vertical Margin
The padding and margin properties are very helpful in adding space between various items on the page.
- Border Width: The border-width property is used to control the width of a border. The value of this property can either be given in pixels or using one of the following values: thin medium thick (You cannot use percentages with this property.
-
Border Style You can control the style of a border using the border-style property. This property can take the following values: solid a single solid line dotted a series of square dots (if your border is 2px wide, then the dots are 2px squared with a 2px gap between each dot) dashed a series of short lines double two solid lines (the value of the border-width property creates the sum of the two lines) groove appears to be carved into the page ridge appears to stick out from the page inset appears embedded into the page outset looks like it is coming out of the screen hidden / none no border is shown
- Border Color You can specify the color of a border using either RGB values, hex codes or CSS color names (as you saw on pages 251-252).
Shorthand
The border property allows you to specify the width, style and color of a border in one property (and the values should be coded in that specific order).
Padding The padding property allows you to specify how much space should appear between the content of an element and its border. The value of this property is most often specified in pixels (although it is also possible to use percentages or ems). If a percentage is used, the padding is a percentage of the browser window (or of the containing box if it is inside another box)
Article The margin property controls the gap between boxes. Its value is commonly given in pixels, although you may also use percentages or ems. If one box sits on top of another, margins are collapsed , which means the larger of the two margins will be used and the smaller will be disregarded.
Centering Content If you want to center a box on the page (or center it inside the element that it sits in), you can set the left-margin and right-margin to auto. In order to center a box on the page, you need to set a width for the box (otherwise it will take up the full width of the page).
Change Inline/Block The display property allows you to turn an inline element into a block-level element or vice versa, and can also be used to hide an element from the page. The values this property can take are: inline This causes a block-level element to act like an inline element. block This causes an inline element to act like a block-level element. inline-block This causes a block-level element to flow like an inline element, while retaining other features of a block-level element. none This hides an element from the page. In this case, the element acts as though it is not on the page at all (although a user could still see the content of the box if they used the view source option in their browser). If you use this property, it is important to note that inline boxes are not supposed to create block-level elements.
Hiding Boxes The visibility property allows you to hide boxes from users but It leaves a space where the element would have been. This property can take two values: hidden This hides the element. visible This shows the element. If the visibility of an element is set to hidden, a blank space will appear in its place.
CSS3: Border Images
The border-image property applies an image to the border of any box. It takes a background image and slices it into nine pieces.
-
CSS3: Box Shadows The box-shadow property allows you to add a drop shadow around a box. It works just like the text-shadow property that you met on page 288. It must use at least the first of these two values as well as a color: Horizontal offset Negative values position the shadow to the left of the box. Vertical offset Negative values position the shadow to the top of the box. Blur distance If omitted, the shadow is a solid line like a border. Spread of shadow If used, a positive value will cause the shadow to expand in all directions, and a negative value will make it contract.
-
CSS3: Rounded Corners CSS3 introduces the ability to create rounded corners on any box, using a property called border-radius. The value indicates the size of the radius in pixels. Older browsers that do not support this property will show a box with right-angled corners.
-
CSS3: Elliptical Shapes To create more complex shapes, you can specify different distances for the horizontal and the vertical parts of the rounded corners.
JavaScript
Arrays
- Arrays are special types of variables that store more than one piece of related information.
You create an array and give it a name just like you would any other variable (using the var keyword followed by the name of the array).
- Values in an array are accessed as if they are in a numbered list. It is important to know that the numbering of this list starts at zero (not one).
- You can ACCESSING & CHANGING VALUES IN AN ARRAY
if … else statements
if … else statements allow you to run one set of code if a condition is true, and another if it is false. switch statements allow you to compare a value against possible outcomes (and also provides a default option if none match).
- if … e1se statement allows you to provide two sets of code:
- one set if the condition evaluates to true
- another set if the condition is false IF … ELSE
- There is no need to provide an el se option. (You can just use an if statement.)
- With a series of if statements, they are all checked even if a match has been found (so it performs more slowly than switch).
SWITCH STATEMENTS
A switch statement starts with a variable called the switch value. Each case indicates a possible value for this variable and the code that should run if the variable matches that value.
- In SWITCH You have a default option that is run if none of the cases match.
- If a match is found, that code is run; then the break statement stops the rest of the switch statement running (providing better performance than multiple i f statements).

TYPE COERCION & WEAK TYPING If you use a data type JavaScript did not expect, it tries to make sense of the operation rather than report an error. JavaScript can convert data types behind the scenes to complete an operation. This is known as type coercion.
TRUTHY & FALSY VALUES Due to type coercion, every value in JavaScript can be treated as if it were true or false; and this has some interesting side effects CHECKING EQUALITY & EXISTENCE Because the presence of an object or array can be considered truthy, it is often used to check for the existence of an element within a page. SHORT CIRCUIT VALUES Logical operators are processed left to right. They short-circuit (stop) as soon as they have a result - but they return the value that stopped the processing (not necessarily true or false).
LOOPS
Loops are used in JavaScript to perform repeated tasks based on a condition. Conditions typically return true or false when analysed. A loop will continue running until the defined condition returns false.
The three most common types of loops are:
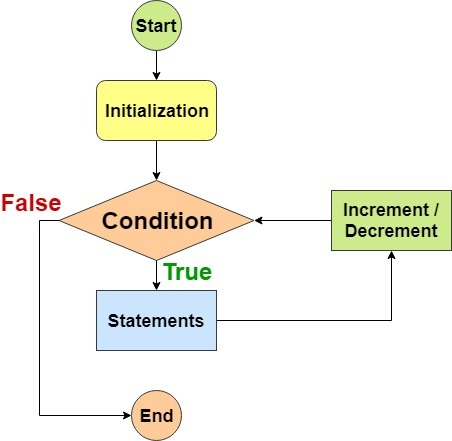
1- For
If you need to run code a speciific number of times , use a for loop. in a for loop , the condition is usually a counter which is used to tell how many times the loop should run
INITIALIZATION , CONDITION, UPDATE
2- while
If you do not know how many times the code should run , you can use a while loop. Here the condition can be something other than counter, and the code will continue to loop foras long as the condition is true
using while loops

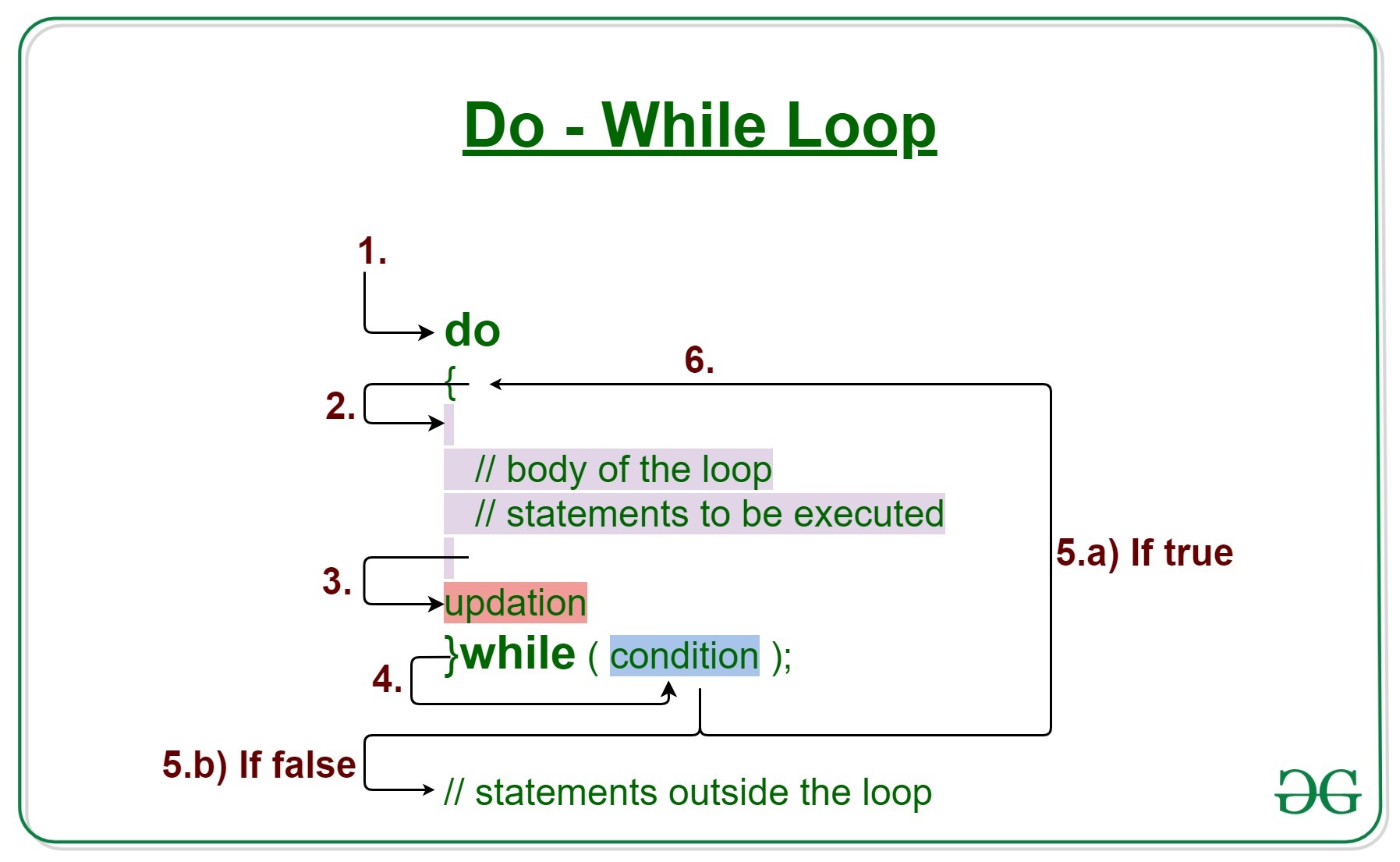
3- do while
The do…while loop is very similar to the while loop, but hasone key difference: itwill always run the statements inside the curly braces at least once, even if the condition evaluates to false.