Hash Tables
What is a Hashtable?
Terminology:
- Hash - A hash is the result of some algorithm taking an incoming string and converting it into a value that could be used for either security or some other purpose. In the case of a hashtable, it is used to determine the index of the array.
- Buckets - A bucket is what is contained in each index of the array of the hashtable. Each index is a bucket. An index could potentially contain multiple key/value pairs if a collision occurs.
- Collisions - A collision is what happens when more than one key gets hashed to the same location of the hashtable.
Structure
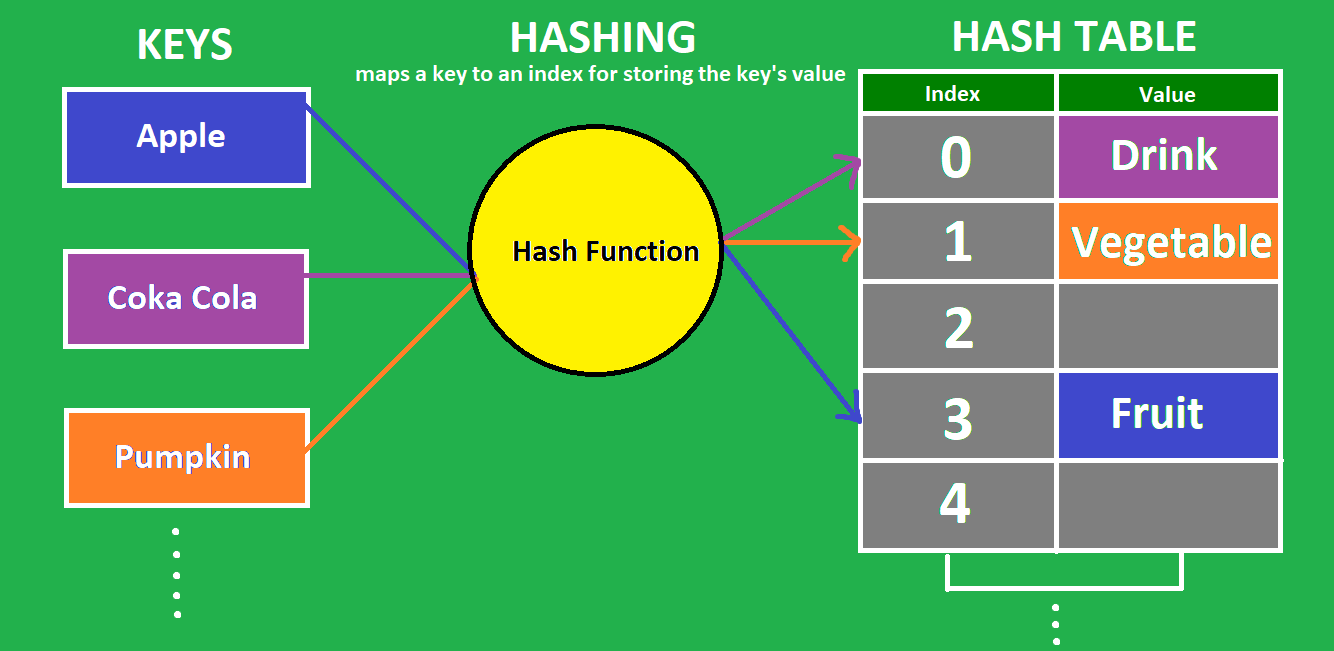
Hashing Basically, a hash code turns a key into an integer. It’s very important that hash codes are deterministic: their output is determined only by their input. Hash codes should never have randomness to them. The same key should always produce the same hash code.
Creating a Hash A hashtable traditionally is created from an array. I always like the size 1024. this is important for index placement. After you have created your array of the appropriate size, do some sort of logic to turn that “key” into a numeric number value. Here is a possible suggestion:
- Add or multiply all the ASCII values together.
- Multiply it by a prime number such as 599.
- Use modulo to get the remainder of the result, when divided by the total size of the array.
- Insert into the array at that index.
Internal Methods
Add()
When adding a new key/value pair to a hashtable:
send the key to the GetHash method. Once you determine the index of where it should be placed, go to that index Check if something exists at that index already, if it doesn’t, add it with the key/value pair. If something does exist, add the new key/value pair to the data structure within that bucket.
Find()
The Find takes in a key, gets the Hash, and goes to the index location specified. Once at the index location is found in the array, it is then the responsibility of the algorithm the iterate through the bucket and see if the key exists and return the value.
Contains()
The Contains method will accept a key, and return a bool on if that key exists inside the hashtable. The best way to do this is to have the contains call the GetHash and check the hashtable if the key exists in the table given the index returned.
GetHash()
The GetHash will accept a key as a string, conduct the hash, and then return the index of the array where the key/value should be placed.
Hashing is a technique that is used to uniquely identify a specific object from a group of similar objects. Some examples of how hashing is used in our lives include:
- In universities, each student is assigned a unique roll number that can be used to retrieve information about them.
- In libraries, each book is assigned a unique number that can be used to determine information about the book, such as its exact position in the library or the users it has been issued to etc.
In both these examples the students and books were hashed to a unique number.

Hash function
A hash function is any function that can be used to map a data set of an arbitrary size to a data set of a fixed size, which falls into the hash table. The values returned by a hash function are called hash values, hash codes, hash sums, or simply hashes.
To achieve a good hashing mechanism, It is important to have a good hash function with the following basic requirements:
-
Easy to compute: It should be easy to compute and must not become an algorithm in itself.
-
Uniform distribution: It should provide a uniform distribution across the hash table and should not result in clustering.
-
Less collisions: Collisions occur when pairs of elements are mapped to the same hash value. These should be avoided.