Trees
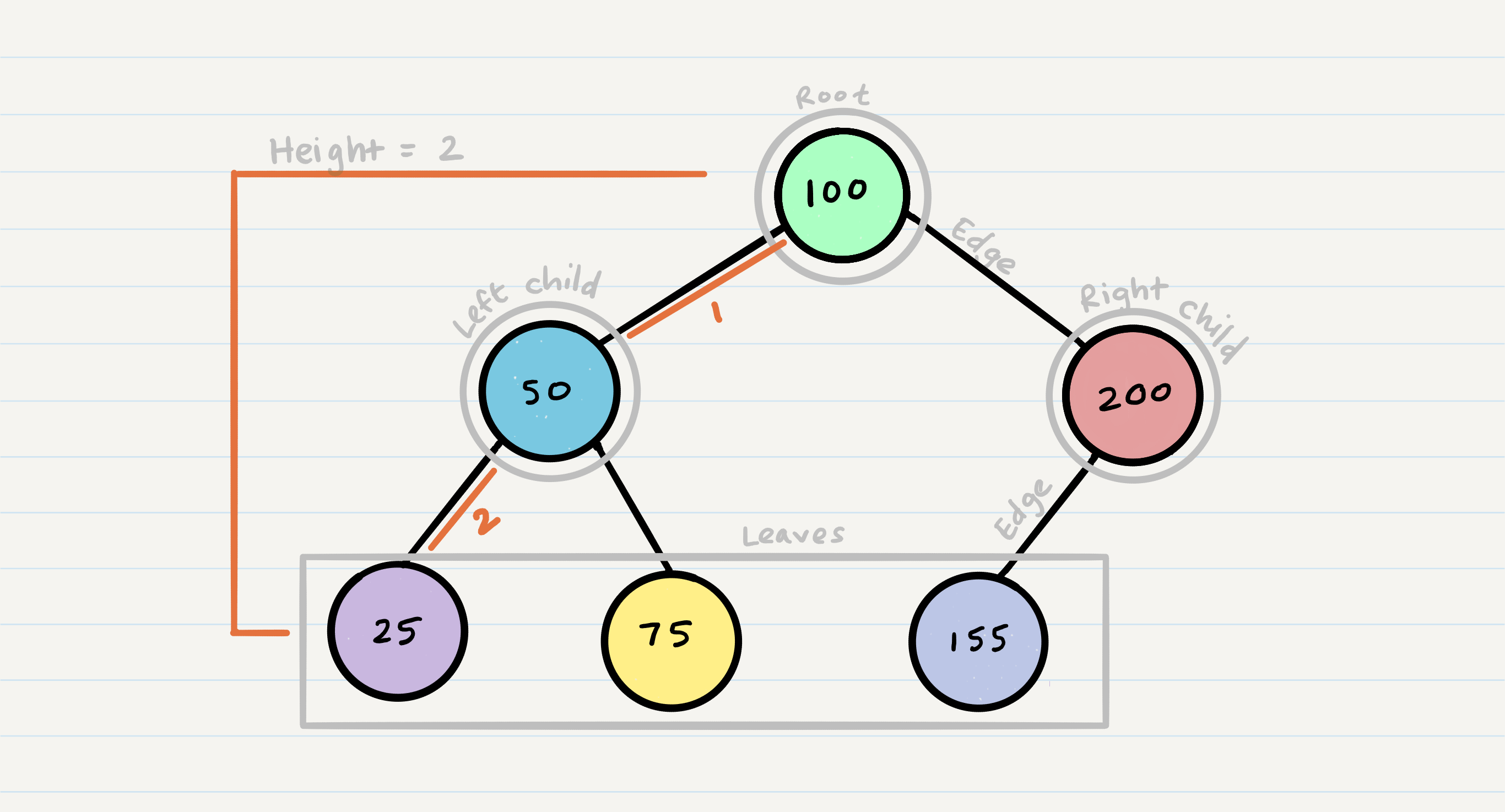
Node - A Tree node is a component which may contain it’s own values, and references to other nodes Root - The root is the node at the beginning of the tree K - A number that specifies the maximum number of children any node may have in a k-ary tree. In a binary tree, k = 2. Left - A reference to one child node, in a binary tree Right - A reference to the other child node, in a binary tree Edge - The edge in a tree is the link between a parent and child node Leaf - A leaf is a node that does not have any children Height - The height of a tree is the number of edges from the root to the furthest leaf
Sample Tree
Traversals
An important aspect of trees is how to traverse them. Traversing a tree allows us to search for a node, print out the contents of a tree, and much more! There are two categories of traversals when it comes to trees:
Depth First
Breadth Firs:
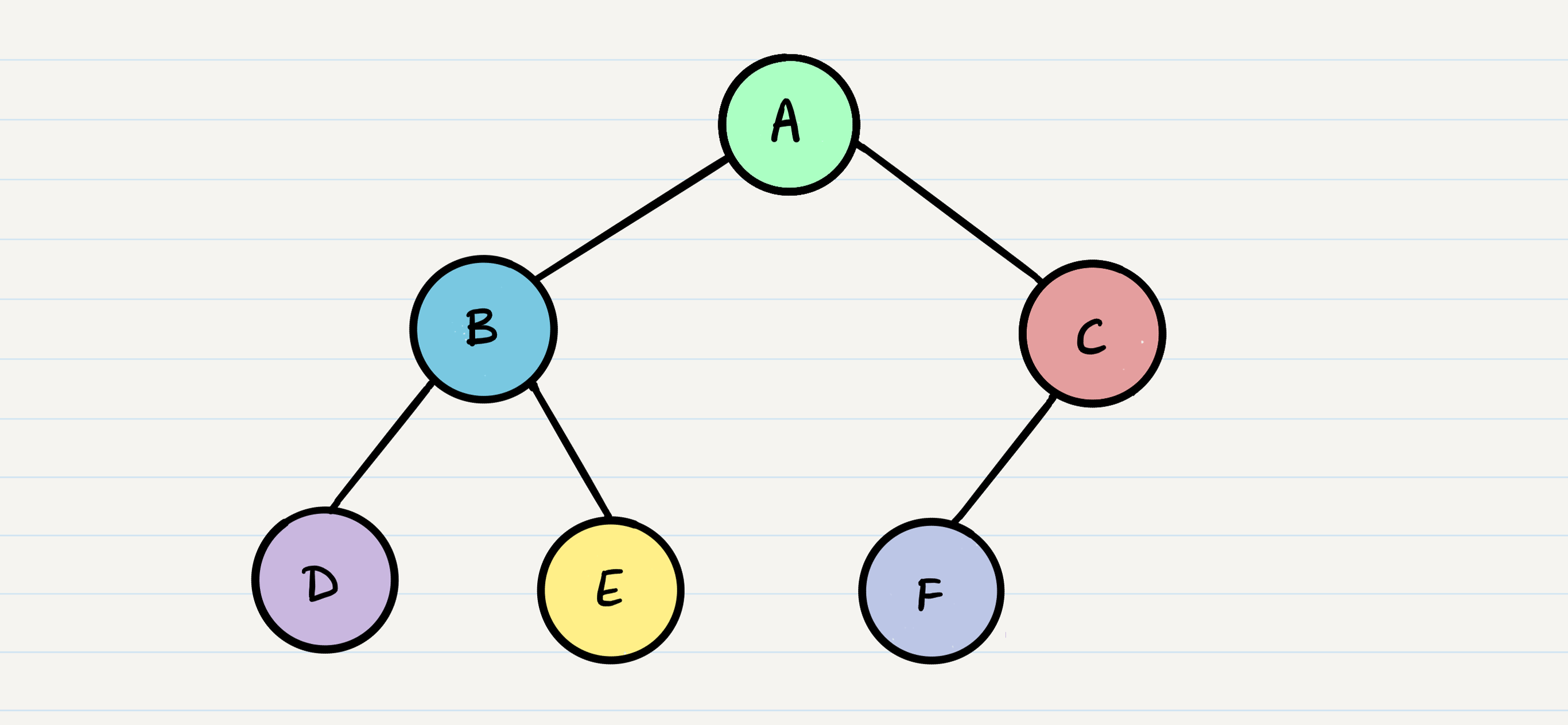
Breadth first traversal iterates through the tree by going through each level of the tree node-by-node. So, given our starting tree one more time:

Our output using breadth first traversal is now:
Output: A, B, C, D, E, F
Traditionally, breadth first traversal uses a queue (instead of the call stack via recursion) to traverse the width/breadth of the tree. Let’s break down the process.
Binary Tree Vs K-ary Trees
In all of our examples, we’ve been using a Binary Tree. Trees can have any number of children per node, but Binary Trees restrict the number of children to two (hence our left and right children).
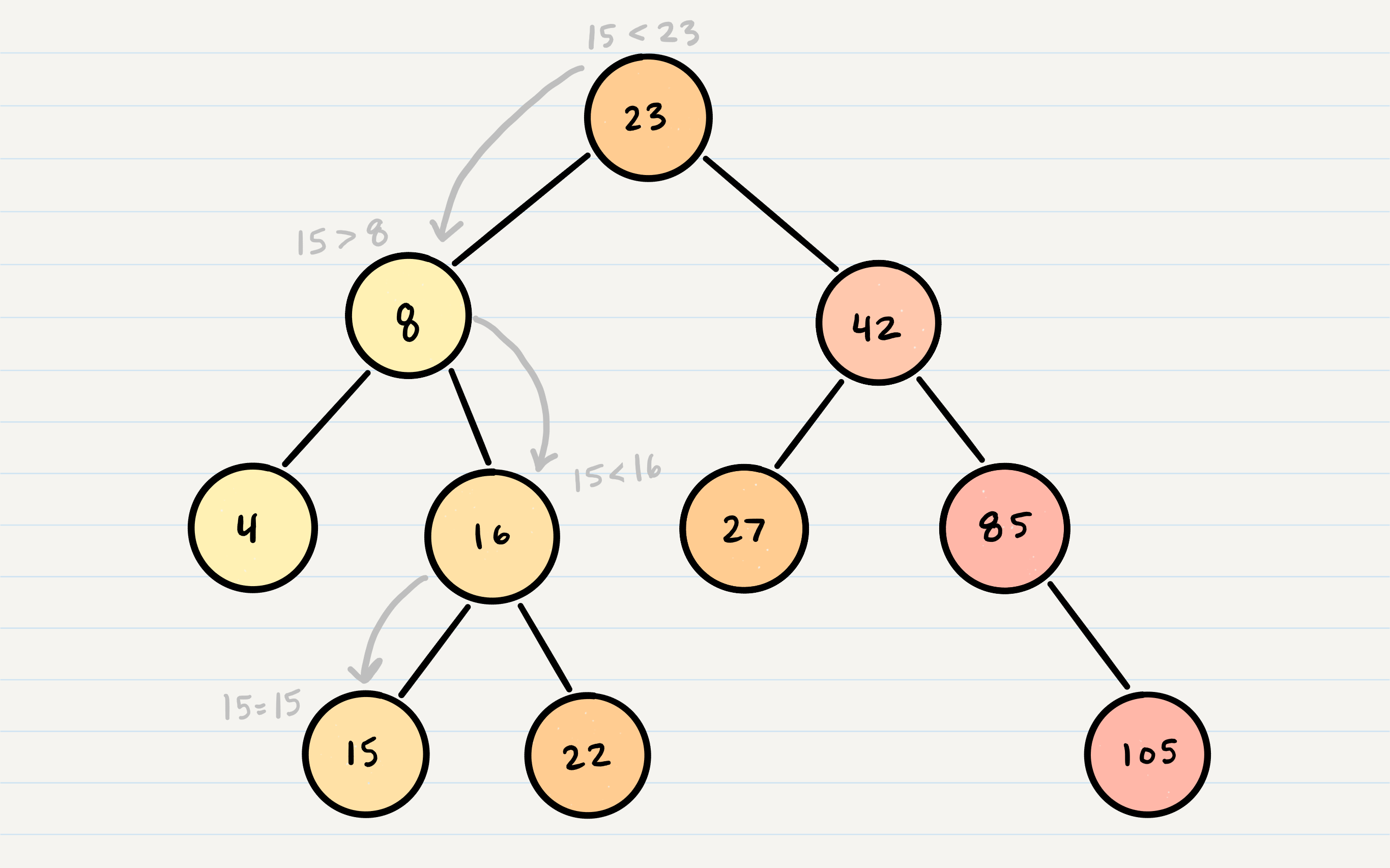
Binary Search Trees
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a type of tree that does have some structure attached to it. In a BST, nodes are organized in a manner where all values that are smaller than the root are placed to the left, and all values that are larger than the root are placed to the right.
Big O The Big O time complexity of a Binary Search Tree’s insertion and search operations is O(h), or O(height). In the worst case, we will have to search all the way down to a leaf, which will require searching through as many nodes as the tree is tall. In a balanced (or “perfect”) tree, the height of the tree is log(n). In an unbalanced tree, the worst case height of the tree is n.
The Big O space complexity of a BST search would be O(1). During a search, we are not allocating any additional space.